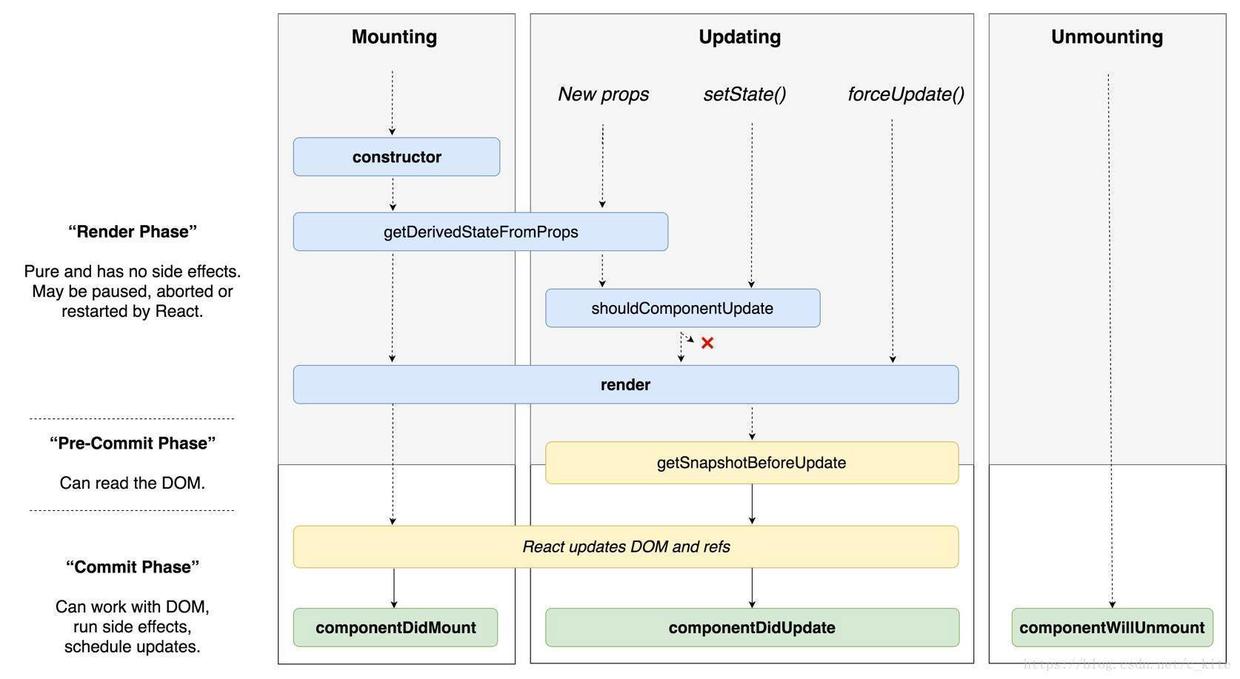
新生命周期
创建组件时的生命周期
创建过程
- parent constructor
- parent getDerivedStateFromProps
- parent render
- Child constructor
- Child getDerivedStateFromProps
- Child render
- Child componentDidMount
- parent componentDidMount
说明
getDerivedStateFromProps的参数为nextProps, prevState- 这个方法将会在组件实例化和接收到新的
props的时候被调用. 而componentWillReceiveProps只会在接收到新的props的时候才会调用 - 当组件实例化的时候,这个方法替代了
componentWillMount(),而当接收到新的props时,该方法替代了componentWillReceiveProps()和componentWillUpdate() - 这个方法是个
static的方法,因此使用this在这个方法中并不指代本实例组件,如果打印出来会发现这个this在这个方法中是null. 而且这个方法会返回值. 当需要更新状态时,需要返回一个object,如果不需要任何更新,则返回null即可 - 如果由于父组件的原因导致该组件重新渲染,这个方法也会被调用,如果只想要处理更新的话,最好加上判断条件
if (nextProp !== prevProp).另外,虽然this.setState()也会导致组件重新渲染,但并不会导致这个方法的重新调用.
正式版的context API
使用context
1
2
3
4
5
6import React, { createContext } from 'react';
const ctx = createContext({
msg: 'hello world!',
});
const { Provider, Consumer } = ctx;Provider组件用于将context数据传给该组件树下的所有组件value属性是context的内容
要使用context的数据,我们需要使用Consumer组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44// 数据提供者
class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Provider value={{ msg: 'hello react!' }}>
<ChildComponent1 />
<ChildComponent2 />
</Provider>
<ChildComponent3 />
</div>
);
}
}
// 数据消费者
// 函数式
const ChildComponent1 = () => (
<Consumer>
{context => <p>{context.msg}</p>}
</Consumer>
);
// 类
class ChildComponent2 extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Consumer>
{context => <p>{context.msg}</p>}
</Consumer>
);
}
}
// 类
class ChildComponent3 extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Consumer>
{context => <p>{context.msg}</p>}
</Consumer>
);
}
}
/*
Consumer下不能写其它的东西,比如<Consumer>Message:{context => <p>{context.msg}</p>}</Consumer> 只能是一个函数 返回需要渲染的组件
*/既然context的内容是写在Provider的value中,如果没有将Consumer作为Provider的子组件, 如上面的ChildComponent3,那么Consumer将使用创建context时的参数作为context
Provider 和 Consumer 必须来自同一次 React.createContext 调用。也就是说 NameContext.Provider 和 AgeContext.Consumer 是无法搭配使用的。
React.createContext 方法接收一个默认值作为参数。当 Consumer 外层没有对应的 Provider 时就会使用该默认值。
Provider 组件的 value prop 值发生变更时,其内部组件树中对应的 Consumer 组件会接收到新值并重新执行 children 函数。此过程不受 shouldComponentUpdete 方法的影响。
Provider 组件利用 Object.is 检测 value prop 的值是否有更新。注意 Object.is 和 === 的行为不完全相同。
Consumer 组件接收一个函数作为 children prop 并利用该函数的返回值生成组件树的模式被称为 Render Props 模式。