一个精简、高效且可扩展的状态管理方案,它巧妙地运用了简化的 Flux 原则。该方案提供了一套基于 Hooks 的直观 API,既简洁易用,又避免了冗余代码和强制性的框架偏好,让开发者能够更专注于业务逻辑的实现。
Flux 原则
Flux 原则主要围绕“单向数据流”这一核心概念展开,旨在通过清晰的数据流和组件间的解耦来提高应用的可维护性和可扩展性。
单向数据流
- 定义:在 Flux 应用中,数据的变化严格遵循单一方向流动的原则,即数据只能从一个源头流出,经过一系列的处理后,最终更新到视图层进行展示。
- 作用:单向数据流有助于减少数据流向的复杂性,使得数据的变化更加可预测和易于追踪。
核心组成部分
Flux 架构通常包括四个核心组成部分:View(视图)、Action(动作)、Dispatcher(分发器)和 Store(存储器)。
- View(视图):负责渲染 UI 界面,并通过用户交互产生 Action。
- Action(动作):是一个包含了类型(type)和数据的对象,用于描述发生了什么。Action 是数据变化的唯一来源。
- Dispatcher(分发器):接收 Action,并将其分发给所有已注册的回调函数。Dispatcher 本身不存储任何数据或状态。
- Store(存储器):负责存储应用的状态,并根据接收到的 Action 来更新状态。Store 是应用状态的唯一来源。
工作流程
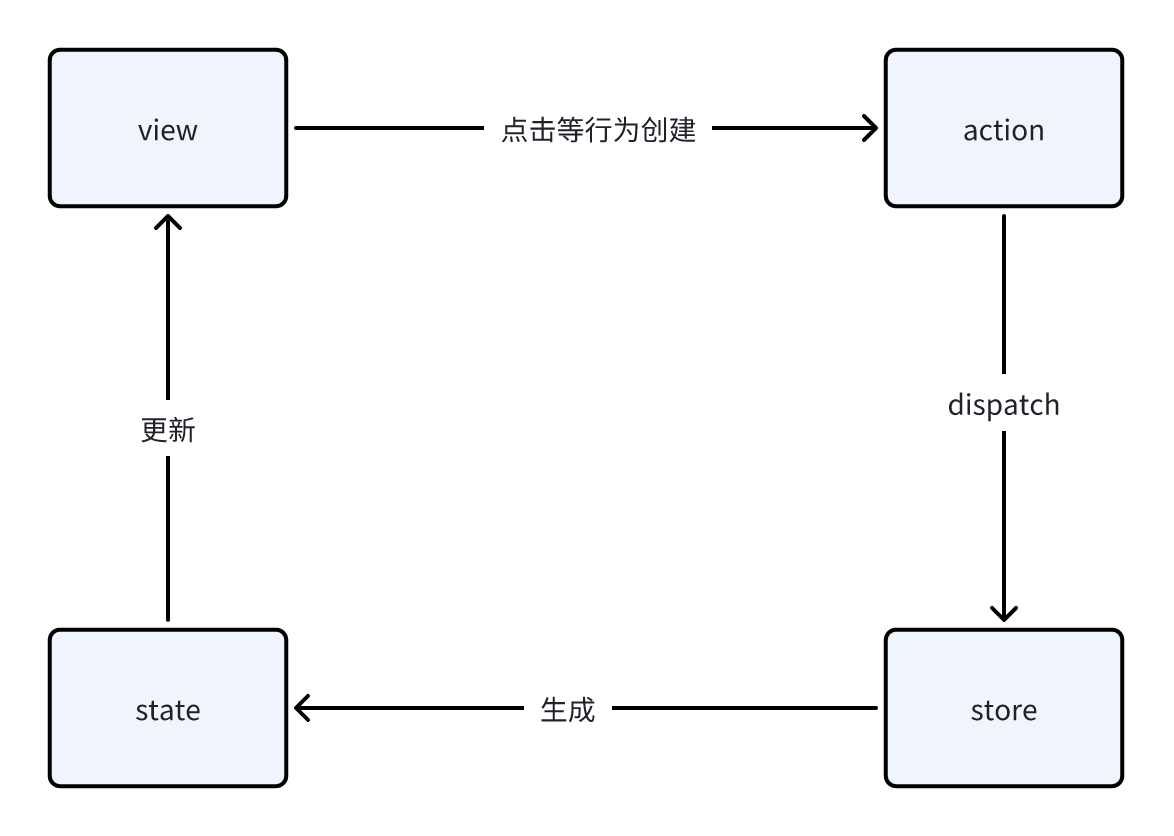
- 当用户在视图层进行交互时,会产生一个 Action。
- Action 被发送到 Dispatcher。
- Dispatcher 将 Action 广播给所有已注册的 Store。
- Store 根据 Action 的类型和内容来更新自身的状态。
- Store 更新状态后,会通知视图层进行相应的渲染。
优点
- 预测性:由于数据变化遵循严格的单向流动,因此可以更容易地预测应用的状态变化。
- 解耦:View、Action、Dispatcher 和 Store 之间相对独立,降低了组件间的耦合度。
- 可维护性:清晰的数据流和组件间的解耦使得应用更加容易维护和扩展。
Hooks
内部通过 useSyncExternalStore 实现,useSyncExternalStore 一个让你订阅外部 store 的 React Hook
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
let nextId = 0
let todos = [{ id: nextId++, text: 'Todo #1' }]
let listeners = []
export const todosStore = {
addTodo() {
todos = [...todos, { id: nextId++, text: 'Todo #' + nextId }]
emitChange()
},
subscribe(listener) {
listeners = [...listeners, listener]
return () => {
listeners = listeners.filter((l) => l !== listener)
}
},
getSnapshot() {
return todos
},
}
function emitChange() {
for (let listener of listeners) {
listener()
}
}
import { useSyncExternalStore } from 'react'
import { todosStore } from './todoStore.js'
export default function TodosApp() {
const todos = useSyncExternalStore(
todosStore.subscribe,
todosStore.getSnapshot
)
return (
<>
<button onClick={() => todosStore.addTodo()}>Add todo</button>
<hr />
<ul>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<li key={todo.id}>{todo.text}</li>
))}
</ul>
</>
)
}
|
使用
支持能力
- 异步请求
- 组件外订阅更新
- 框架无关
- Immer 支持
- 持久化
- Reducer
- devtools
函数式组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import { create } from 'zustand'
const useBearStore = create((set) => ({
bears: 0,
increasePopulation: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 })),
removeAllBears: () => set({ bears: 0 }),
}))
function BearCounter() {
const bears = useBearStore((state) => state.bears)
return <h1>{bears} around here ...</h1>
}
|
类组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| import { create } from 'zustand'
const useBearStore = create((set) => ({
bears: 0,
increasePopulation: () => set((state) => ({ bears: state.bears + 1 })),
removeAllBears: () => set({ bears: 0 }),
}))
class BearCounter extends React.Component {
componentDidMount() {
this.unSub = useBearStore.subscribe(this.handleSubscribe)
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unSub()
}
handleSubscribe = (store) => {
this.setState({ bears: store.bears })
}
render() {
const { bears } = this.state
return <h1>{bears} around here ...</h1>
}
}
|
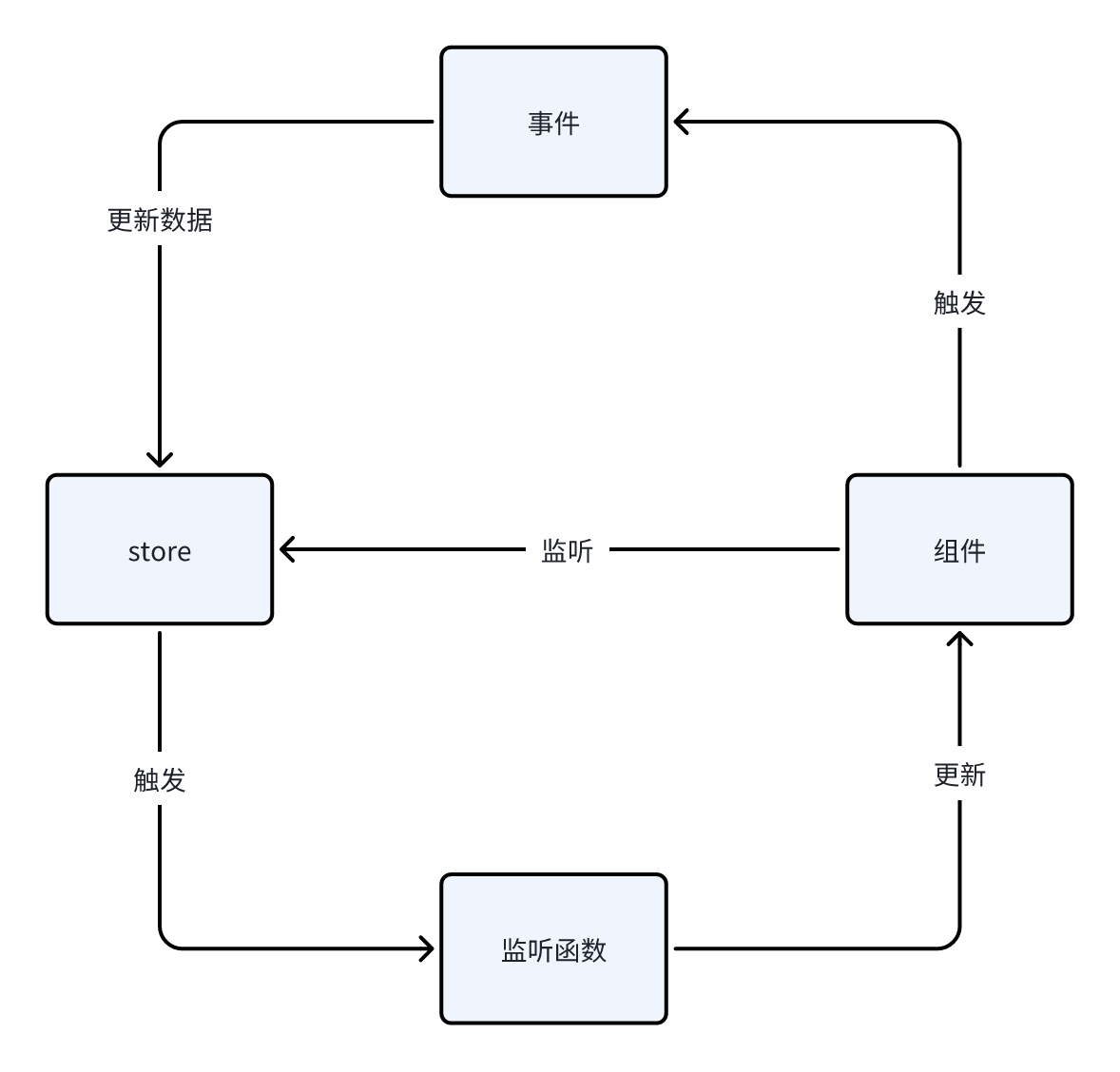
实现
创建 store
利用闭包构建一个 store ,通过发布订阅的方式实现更新的监听
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| const createStoreImpl: CreateStoreImpl = (createState) => {
type TState = ReturnType<typeof createState>
type Listener = (state: TState, prevState: TState) => void
let state: TState
const listeners: Set<Listener> = new Set()
const setState: StoreApi<TState>['setState'] = (partial, replace) => {
const nextState =
typeof partial === 'function'
? (partial as (state: TState) => TState)(state)
: partial
if (!Object.is(nextState, state)) {
const previousState = state
state =
replace ?? (typeof nextState !== 'object' || nextState === null)
? (nextState as TState)
: Object.assign({}, state, nextState)
listeners.forEach((listener) => listener(state, previousState))
}
}
const getState: StoreApi<TState>['getState'] = () => state
const getInitialState: StoreApi<TState>['getInitialState'] = () =>
initialState
const subscribe: StoreApi<TState>['subscribe'] = (listener) => {
listeners.add(listener)
return () => listeners.delete(listener)
}
const api = { setState, getState, getInitialState, subscribe }
const initialState = (state = createState(setState, getState, api))
return api as any
}
|
React 订阅更新
利用 useSyncExternalStore 订阅更新
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| export function useStore<TState, StateSlice>(
api: ReadonlyStoreApi<TState>,
selector: (state: TState) => StateSlice = identity as any
) {
const slice = React.useSyncExternalStore(
api.subscribe,
() => selector(api.getState()),
() => selector(api.getInitialState())
)
React.useDebugValue(slice)
return slice
}
|
中间件
通过高阶函数的方式实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| const reduxImpl = (reducer, initial) => (set, _get, api) => {
api.dispatch = (action) => {
set((state) => reducer(state, action), false, action)
return action
}
api.dispatchFromDevtools = true
return { dispatch: (...a) => api.dispatch(...a), ...initial }
}
|
参考

