有限状态机
定义
有限状态机是一个五元组 (Q, Σ ,δ, q0, F):
- Q 是一个有穷集合,叫 状态集
- Σ 是一个有穷集合,叫 字母表
- δ : Q × Σ → Q 是 转移函数
- q0 ∈ Q 是 起始状态.
- F ⊆ Q 是 接受状态
执行流程
从开始状态,根据不同的输入,自动进行状态转移的过程,直到进入接受状态为止
确定有限状态自动机(DFA)
DFA 的每一个状态对于字母表中的每一个符号总是恰好有一个转移箭头射出。其确定性在于,在一个状态下,输入一个符号,一定是转移到确定的状态,没有其他的可能性
非确定有限状态自动机(NFA)
NFA 中每一个状态对于字母表的每一个符号(如:0/1)可能有多个箭头射出。其不确定性在于,在一个状态下,输入一个符号,可能转移到 n 个状态,出现了多种状态转移。另外 NFA 中箭头的标号可以是 ε(空转移,即:未输入任何符号也可转移到另一个状态)
组成部分
- 解析器:负责解析正则表达式字符串,将其转换为内部表示形式,如状态机、有向图等。
- 状态机:根据解析器生成的内部表示形式,构建一个有限状态自动机,用于在文本中搜索匹配项。
- 匹配器:利用状态机在输入文本中进行匹配,根据正则表达式的模式和规则,找到符合条件的子串。
- 捕获器:用于捕获匹配过程中产生的结果,如分组捕获、非捕获组等。
- 替换器:用于执行替换操作,根据正则表达式中的替换规则,将匹配的子串替换为新的内容。
执行流程
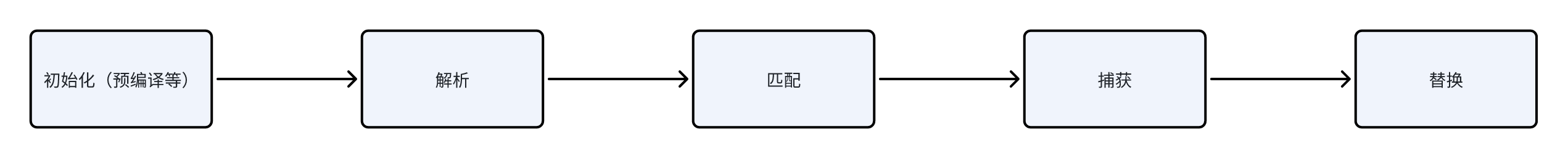
代码实现思路
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
| class Value {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
}
equal = (char) => {
return char === this.value
}
}
class Token {
constructor(value, meta) {
this.value = new Value(value)
this.meta = meta
}
matchMeta = (c) => {
return this.meta && this.value.equal(c)
}
matchChar = (c) => {
return !this.meta && this.value.equal(c)
}
match = (c) => {
if (this.matchMeta('.')) {
return typeof c !== 'undefined'
} else {
return this.matchChar(c)
}
}
}
class MyPattern {
constructor(tokens, matchString) {
this.tokens = tokens
this.matchString = matchString
}
matchStar = (i, j) => {
const token = this.tokens[i]
const ch = this.matchString[j]
if (token && token.match(ch) && this.matchStar(i, j + 1)) {
return true
} else {
return this.matchStr(i + 2, j)
}
}
matchStr = (i, j) => {
const token = this.tokens[i]
const nextToken = this.tokens[i + 1]
if (token && token.matchMeta('$')) {
return j >= this.matchString.length
} else if (token && nextToken && nextToken.matchMeta('*')) {
return this.matchStar(i, j)
} else if (token && token.match(this.matchString[j])) {
return this.matchStr(i + 1, j + 1)
}
return false
}
match() {
if (this.matchStr(1, 0)) {
return true
}
return false
}
}
class MyRegexp {
constructor(regexp) {
this.regexp = regexp
}
compile = () => {
this.tokens = []
for (let i = 0; i < this.regexp.length; i++) {
switch (this.regexp[i]) {
case '*': {
this.tokens.push(new Token('*', true))
break
}
case '^': {
this.tokens.push(new Token('^', true))
break
}
case '$': {
this.tokens.push(new Token('$', true))
break
}
case '.': {
this.tokens.push(new Token('.', true))
break
}
default: {
this.tokens.push(new Token(this.regexp[i], false))
break
}
}
}
}
match = (str) => {
if (!this.tokens) {
this.compile()
}
return new MyPattern(this.tokens, str).match()
}
}
|
参考
